Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based service that focuses on MDM (Mobile Device Management) and MAM (Mobile Application Management). It allows you to control how organizational devices such as phones, tablets, and laptops are used. Specific policies can be configured to control applications, for example, preventing emails from being sent to people outside the organization.
Intune is part of the Enterprise Mobility + Security suite and integrates with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) to control which users have access and what they can access.
For data protection, it integrates with Azure Information Protection. Intune can also be used with Microsoft 365 products, enabling the deployment of Teams, OneNote, and other Microsoft 365 apps to devices.
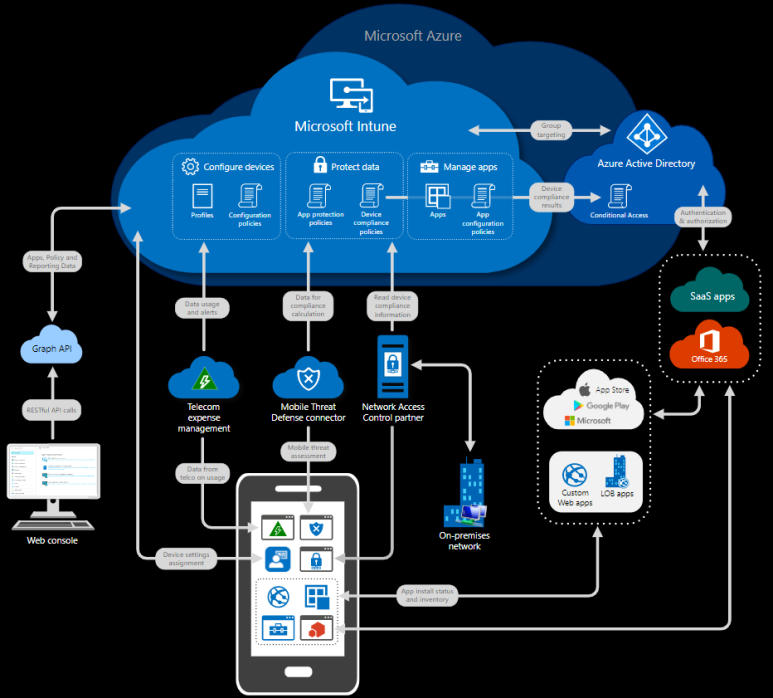
Source: Microsoft Intune이란? | Microsoft Docs
Capabilities of Intune:
- Choose between using Intune 100% in the cloud or selecting co-management with Configuration Manager and Intune.
- Set rules and configure devices, whether personal or organizational, to access data and networks.
- Deploy and authenticate apps on devices (both on-premise and mobile).
- Control how users access and share information.
- Ensure that devices and apps comply with company security requirements.
Device Management (MDM):
Devices and their users must be enrolled in Intune. They will receive rules and settings through policies configured in Intune.
For example, tasks such as setting password and PIN requirements, creating VPN connections, and configuring threat prevention can be performed.
For personal devices or BYOD (Bring Your Own Devices), users may not grant full permissions to the organization's administrators. In this approach, users are given options. If they want full access to organizational resources, they must enroll the device. If they only need access to email or Teams, apps requiring MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) can be used.
Administrators can:
- View enrolled devices and retrieve an inventory of devices accessing organizational resources.
- Configure devices to meet security and health standards.
- Push certificates to devices so users can access Wi-Fi networks or connect to the network using a VPN.
- Remove organizational data from devices in cases of loss, theft, or when the device is no longer in use.
Application Management (MAM):
MAM is designed to protect organizational data at the application level.
Administrators can:
- Add and assign mobile apps to user groups and devices, including specific user groups or devices.
- Configure apps to launch or run with specific settings and update existing apps on devices.
- View reports on app usage and track usage statistics.
- Perform selective wipes, removing only organizational data from apps.
One method of providing mobile app security is through app protection policies.
- Using Azure AD ID, organizational data is separated from personal data. Personal information is isolated from the organization’s IT awareness. Additional security measures are applied to data accessed using organizational credentials.
- Restrict actions users can perform, such as copying, pasting, saving, and viewing, to protect access to personal devices.
- These policies can be created and deployed to devices enrolled in Intune, registered in other MDM services, or even to unenrolled devices.
For example, when a user logs into a device with organizational credentials, they can access data that is otherwise denied to their personal ID. Once organizational data is accessed, app protection policies control how that data can be stored and shared.
When a user logs in with a personal ID, the same protections are not applied.
'IT' 카테고리의 다른 글
| International Dedicated Line (0) | 2022.09.26 |
|---|---|
| 네트워크 구성도 (1) | 2022.09.26 |
| SAP Consignment Process (SD Module) (0) | 2022.09.26 |
| iPhone Security Certificate Error Guide (0) | 2022.09.26 |
| Deleting Cookies in Chrome (0) | 2022.09.26 |


